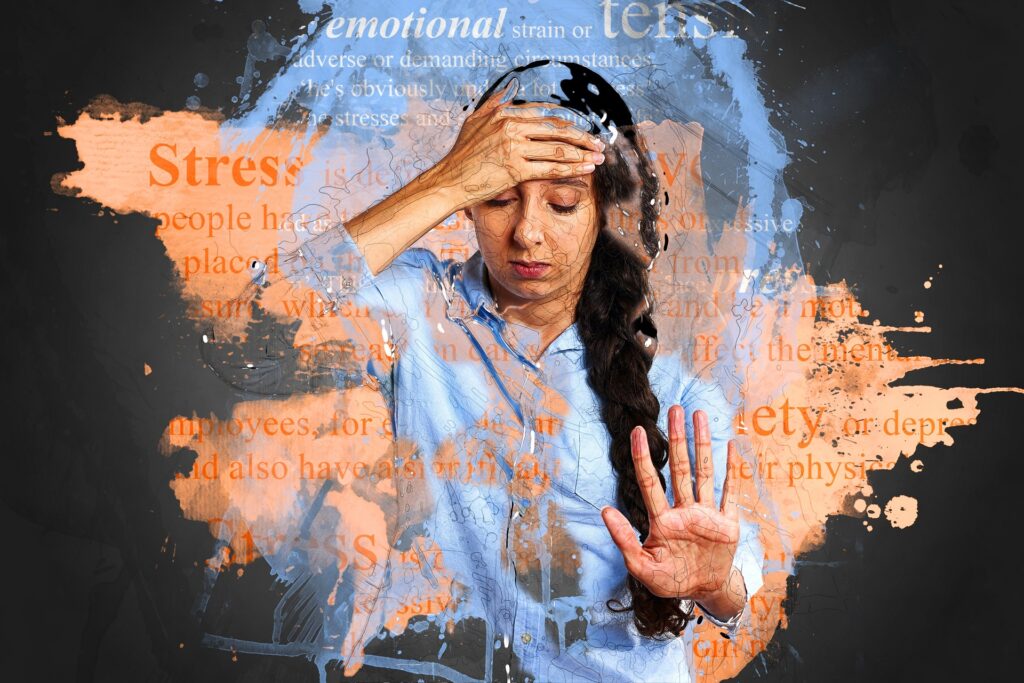
Anxiety disorders encompass a wide range of conditions characterized by excessive worry, fear, and apprehension. From generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) to panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias, anxiety can manifest in various ways, affecting both mental and physical well-being. Understanding anxiety is crucial for managing and recovering from it. Here’s a detailed exploration of strategies to help you navigate anxiety:
- Seek professional help: Anxiety can be overwhelming, but you don’t have to face it alone. Seeking professional help from a licensed therapist or counselor is a critical step toward managing and recovering from anxiety. These professionals are trained to provide evidence-based treatments, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which can help you understand the underlying causes of your anxiety and develop effective coping strategies.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): CBT is a widely recognized therapeutic approach for treating anxiety disorders. It focuses on identifying and challenging irrational thoughts and beliefs that contribute to anxiety, as well as teaching practical skills to manage symptoms. Through CBT, you can learn to reframe negative thinking patterns and develop healthier ways of coping with stress and anxiety.
- Mindfulness-based techniques: Mindfulness practices, such as mindfulness meditation and mindful breathing, can help reduce anxiety symptoms by promoting present-moment awareness and acceptance. By learning to observe your thoughts and emotions without judgment, you can cultivate a greater sense of calm and resilience in the face of anxiety triggers.
- Practice self-care: Taking care of your physical and emotional well-being is essential for managing anxiety. Make self-care a priority by prioritizing activities that promote relaxation and stress relief.
- Healthy lifestyle habits: Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as getting regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, and prioritizing sleep, can have a significant impact on your anxiety levels. Exercise, in particular, has been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety by releasing endorphins and promoting a sense of well-being.
- Stress management techniques: Explore different stress management techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery. These techniques can help calm your nervous system and reduce the physical symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heartbeat and shallow breathing.
- Challenge negative thoughts: Anxiety often stems from distorted or exaggerated thoughts and beliefs about potential threats or dangers. Learning to identify and challenge these negative thoughts is a key aspect of managing anxiety.
- Thought records: Keep a thought diary to track your anxious thoughts and the situations that trigger them. Once you’ve identified a pattern, challenge the accuracy of these thoughts by gathering evidence for and against them. This can help you develop a more balanced and realistic perspective on the situations that cause anxiety.
- Cognitive restructuring: Replace irrational or catastrophic thoughts with more rational and adaptive ones. For example, if you find yourself catastrophizing about a future event, remind yourself of past experiences where things turned out better than you expected. This can help counteract the tendency to overestimate the likelihood of negative outcomes.
- Build a support network: Surround yourself with supportive friends, family members, and peers who understand and validate your experiences with anxiety. Having a strong support network can provide encouragement, empathy, and practical assistance when you need it most.
- Support groups: Consider joining a support group for individuals with anxiety disorders. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can help reduce feelings of isolation and stigma, as well as provide valuable insights and coping strategies.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Incorporate relaxation techniques into your daily routine to help manage stress and anxiety.
- Deep breathing: Practice deep breathing exercises to activate the body’s relaxation response and reduce feelings of tension and anxiety. Try diaphragmatic breathing, where you inhale deeply through your nose, filling your belly with air, and exhale slowly through your mouth.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: Progressive muscle relaxation involves tensing and then relaxing different muscle groups in the body, one at a time. This can help release physical tension and promote a sense of relaxation and calm.
- Set realistic goals: Break down your recovery goals into smaller, achievable steps, and celebrate your progress along the way. Remember that recovery from anxiety is a gradual process, and setbacks are a natural part of the journey.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily life and seeking support from professionals and loved ones, you can learn to manage anxiety effectively and work toward a brighter, more fulfilling future. Remember that recovery is possible, and you are not alone in your journey.