Unveiling Dermatomyositis: The Complexities of a Rare Inflammatory Disorder
In the vast landscape of medical conditions, dermatomyositis stands as a rare and enigmatic entity, characterized by a peculiar blend of skin manifestations and muscle weakness. This autoimmune disease, although infrequent, carries significant burdens for those affected, influencing not only their physical health but also their quality of life and emotional well-being. In this article, we delve into the depths of dermatomyositis, exploring its pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnostic challenges, and current treatment modalities.
Understanding Dermatomyositis: A Journey into the Pathophysiology
Dermatomyositis, a member of the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, involves a complex interplay of autoimmune dysregulation, genetic predisposition, and environmental factors. While the exact etiology remains elusive, experts speculate that an aberrant immune response leads to the deposition of immune complexes within blood vessels, muscles, and skin, triggering inflammation and tissue damage.
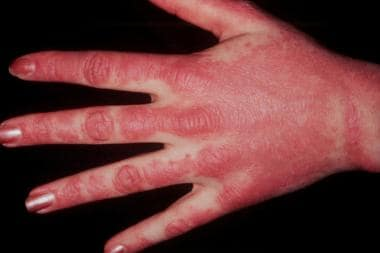
The hallmark skin manifestations of dermatomyositis typically precede or coincide with muscle weakness, serving as early diagnostic clues. Patients often present with a distinctive heliotrope rash, characterized by violaceous discoloration of the eyelids, along with a photosensitive erythema affecting the face, neck, chest, and extensor surfaces of the limbs. Additionally, a Gottron’s sign, manifested by erythematous papules or plaques overlying the knuckles, elbows, and knees, further distinguishes dermatomyositis from other rheumatologic conditions.
Unraveling the Clinical Presentation: Beyond Skin Deep
Beyond its cutaneous manifestations, dermatomyositis manifests as proximal muscle weakness and fatigue, significantly impairing physical function and mobility. Patients often report difficulties with activities of daily living, such as climbing stairs, lifting objects, and combing their hair, reflecting the profound impact of the disease on their independence and self-care abilities.
In severe cases, dermatomyositis can lead to dysphagia, respiratory muscle weakness, and interstitial lung disease, posing grave threats to respiratory function and necessitating vigilant monitoring and intervention. Furthermore, the systemic nature of dermatomyositis may entail extramuscular manifestations, including arthritis, Raynaud’s phenomenon, and cardiac involvement, further complicating the clinical picture and management approach.
Navigating Diagnostic Challenges: The Quest for Clarity
Despite its characteristic features, dermatomyositis often eludes prompt diagnosis, mimicking other autoimmune conditions or systemic disorders. Clinicians must adopt a comprehensive approach, integrating clinical history, physical examination findings, laboratory investigations, and imaging studies to unravel the diagnostic conundrum.
Serologic testing plays a pivotal role in confirming the diagnosis of dermatomyositis, with elevated levels of muscle enzymes such as creatine kinase (CK) and aldolase serving as surrogate markers of muscle inflammation and injury. Additionally, autoantibodies targeting specific antigens, such as anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA), anti-Jo-1, and anti-Mi-2, aid in subtype classification and prognostic stratification.
Imaging modalities, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and muscle biopsy, provide invaluable insights into the extent of muscle involvement, the presence of inflammatory infiltrates, and the degree of fibrosis and atrophy. Notably, the characteristic histopathologic findings of perifascicular atrophy, perivascular inflammation, and immune complex deposition corroborate the diagnosis of dermatomyositis, guiding therapeutic decision-making.
Embracing Therapeutic Strategies: A Multifaceted Approach
The management of dermatomyositis entails a multifaceted approach, aiming to mitigate inflammation, alleviate symptoms, preserve muscle function, and enhance overall quality of life. Pharmacologic interventions form the cornerstone of therapy, with corticosteroids serving as first-line agents to suppress immune-mediated inflammation and modulate disease activity.
In refractory cases or those intolerant to corticosteroids, immunosuppressive agents, such as methotrexate, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, and rituximab, offer alternative therapeutic options to achieve disease remission and minimize long-term complications. Additionally, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) therapy, plasmapheresis, and biologic agents targeting specific cytokines or immune pathways may be considered in select cases, particularly those with severe or recalcitrant disease manifestations.
Beyond pharmacologic interventions, holistic management strategies encompass physical therapy, occupational therapy, and tailored exercise regimens to optimize muscle strength, flexibility, and endurance. Moreover, nutritional support, psychosocial counseling, and patient education initiatives play integral roles in empowering individuals with dermatomyositis to cope with the challenges of their chronic illness and foster resilience and self-efficacy.
Looking Ahead: Advancing Research and Enhancing Care
As our understanding of dermatomyositis continues to evolve, propelled by advances in immunology, genetics, and translational research, the landscape of therapeutic options and diagnostic modalities will undoubtedly expand. Collaborative efforts among clinicians, researchers, advocacy groups, and patients will be instrumental in driving innovation, promoting awareness, and improving outcomes for individuals affected by this rare inflammatory disorder.
In conclusion, dermatomyositis epitomizes the intricate interplay between immune dysregulation, genetic susceptibility, and environmental triggers, culminating in a diverse array of cutaneous, musculoskeletal, and systemic manifestations. Through early recognition, prompt diagnosis, and comprehensive management, clinicians can effectively navigate the complexities of dermatomyositis, empowering patients to lead fulfilling and meaningful lives despite the challenges posed by their chronic illness.